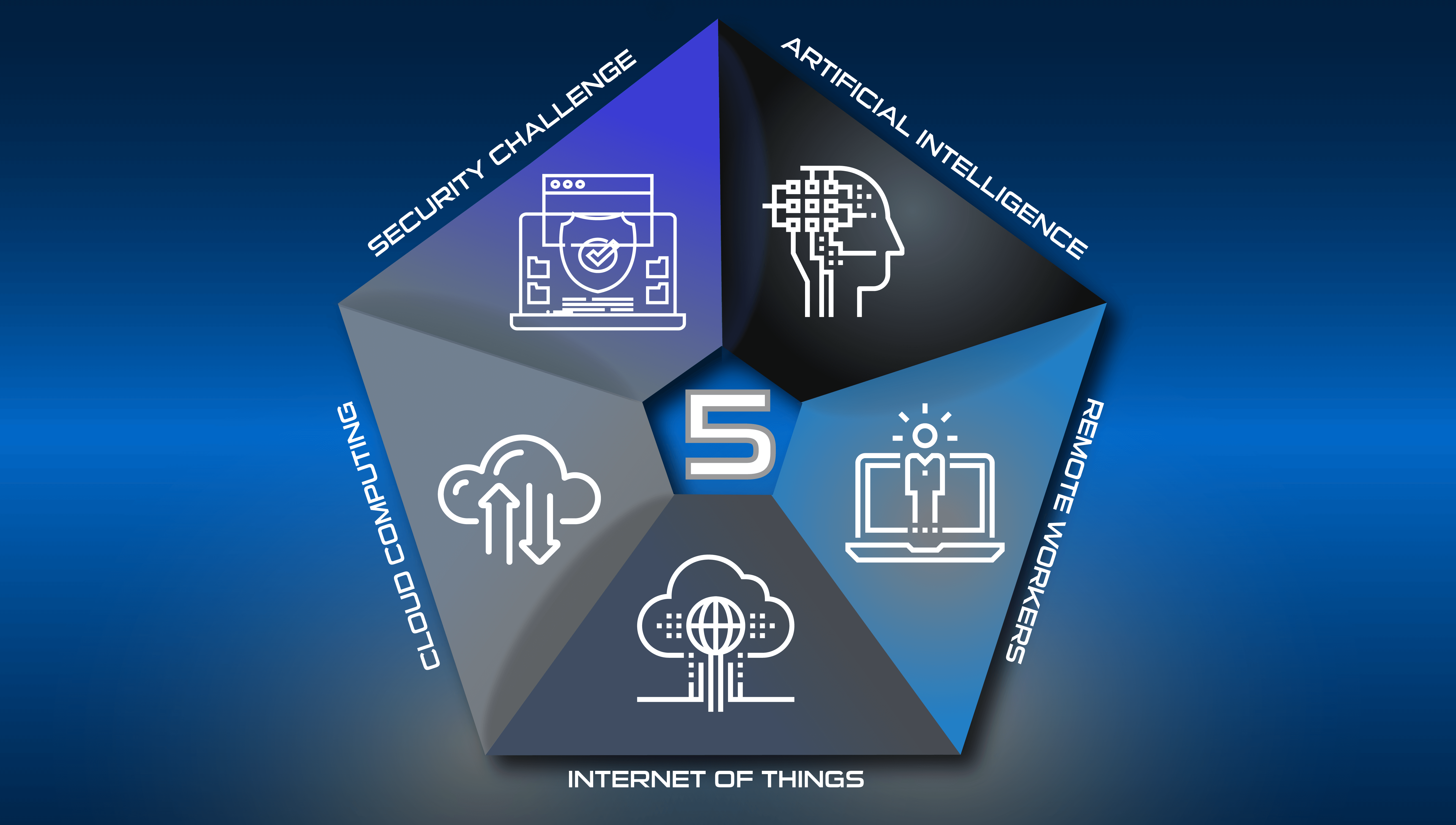
The 5 Tech Revolutions Reshaping Business
What an incredible journey it has been for business owners and managers in recent years, whether navigating through success or battling for every...
4 min read
 Joseph Ugalde
:
Oct 3, 2022 8:20:01 AM
Joseph Ugalde
:
Oct 3, 2022 8:20:01 AM

Nothing is unhackable... This is the one thing we have learned from the decades-long war between the system builders and the hacker "community."
Every program has bugs, every wave can be intercepted and interfered with, and every device can be reverse-engineered. People are also hackable, as we've learned from the evolution of con artists to phishing schemes.
In the last few years, it's been said that two-factor authentication (2FA or MFA) is the answer to many, if not most of the risks of account-thieving hacks. 2FA is great. It pings your phone or email if a hacker tries to login from a new device or location, and you (& your users) have a chance to reject, report, and defend against the hacking attempt. But no system is perfect.
There are already open-sourced strategies to overcome widely used 2FA methods. Fake password updates and spoofed confirmation emails are only the beginning. There are impersonation scams, website proxy logins, duplicated sessions from hacked endpoints, man-in-the-middle interceptions, and even SIM card duplication.
Let's talk about how multi-factor authentication can be phished and how we might keep users safe in spite of this fact.
When the cybersecurity battle was just a technical one, it was security algorithm versus code breaker. Early passwords were guessed or even brute-force cracked. Routing around to the human layer felt like a genius move. 2FA is the ultimate human insulation gap to defeat widespread password theft. But people can be fooled, are busy, and are used to things like bugs, logging back in , login hassle, and technical support asking tedious confirmation questions. It turns out people are easier to hack than machines.
So now, there is a complex network of both technical and scam-artist methods to get around 2FA, just like every other security barrier invented so far. The hacking community is, after all, the ultimate pool of test users. If there is a flaw, a work-around, or a weakness in commonly used business software and methods, they will find it.
2FA was the new kid on the block and it is powerful. A working 2FA system provides security updates and roadblocks that any attentive user can operate to block unknown and unexpected logins. But let's not stop there.
When you place the barrier of human confirmation into the way of hackers, they hack people. What was once called a scam has now become a social hacking method. Lies and impersonations to assist in stealing accounts, infecting victim computers, and accessing protected data through fooling people into thinking they're dealing with someone official.
2-Factor or Multi-Factor Authentication is no more foolproof than any other system, it just increases the visibility of false logins when they occur and adds a layer of complexity to hacking attempts. There are seven (at least) known ways that 2FA can be compromised. The user's device can be compromised so that every keypress and login is hacked. This can lead to duplicate sessions. Man in the Middle hacks can start at a number of points including phishing email, hacked websites, and domain typo-squatting.
If an OTP server is compromised, false and authenticated one time passwords can be sent. Even a user's phone is not a foolproof measure. The technology to duplicate SIM card signals and tap cell and SMS messages has existed for some time now. Likewise, the entire process can be circumvented just with the login credentials for the user's personal email account.
Despite the fact that there are compromises, no system is perfect and 2FA has significantly cut down on the instances of account theft. The two-pronged defense strategy is 1) to keep your technology one step ahead of the hackers with the latest tools and security patches, and 2) to keep your users aware and vigilant against suspicious messages and unexpected confirmation requests.
2-Factor authentication is still an important and widely used part of the cybersecurity landscape. People use and need it, and it absolutely cuts down on stolen accounts. It can also be hacked both technically and socially like most other systems. Nothing is perfect. So here we are defending the "home" team in the great cybersecurity game, we play another round, upgrade your software, and get the team ready for a defensive play.
Contact Systems X for more information about MFA and other cybersecurity solutions.
What an incredible journey it has been for business owners and managers in recent years, whether navigating through success or battling for every...

The role of technology in driving your organization’s success cannot be overstated. As a business owner or IT manager, you rely on your IT support...

Simple antivirus programs are so 2023. In 2024, businesses will face sophisticated cyber threats, including ransomware, phishing attacks, and...