Streamlining ERP Processes: Unlocking the Benefits of Value Stream Mapping
Organizations must optimize processes and improve operational efficiency for sustainable growth in today's competitive landscape. Value stream...
6 min read
 Karen Kiewski
:
Feb 2, 2021 9:27:00 AM
Karen Kiewski
:
Feb 2, 2021 9:27:00 AM

Data migration can be an important part of a business’ IT operations—helping ensure that users within the organization (or its customer base) have access to the data they need after a major change in their IT infrastructure.
What is data migration? What types of data migration processes are there? How long does data migration take? What are some common problems with data migration? What questions should you ask before carrying out a data migration?
Here’s an explanation of data migration that covers the basics of what everyone should know about this IT process:
Put simply, data migration is a business IT process where data is moved from one location, device, format, or application to a different location, device, format, or application.
With such a simple definition, one could say that data migration happens every time someone downloads a file, uploads a completed business document, or sends an attachment in a message. However, data migration in the context of business operations and IT usually means a much larger movement of information—typically as part of a larger IT change.
Examples of such changes could include installing a new data center, changing enterprise applications, or after a business merger when data from both companies needs to be condensed into a single system or workflow.
Data migration can be classified into several types depending on where the data is moving from and where it is going. Some types of data migration include:
RELATED: 14 Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses of Any Size
The length of time that a data migration takes can vary from one migration to another. There are a number of factors that can affect the migration process’ duration. Some examples noted by data giant Google include (this list is paraphrased from Google’s support article):
Basically, if two high-performance servers are used to migrate a relatively small amount of information, the process will likely be very fast. On the other hand, if compatibility issues arise or there are bottlenecks in the data upload/download bandwidth of either asset when moving larger data sets/items, then the process will take longer.
It’s almost impossible to establish an accurate migration timeline without specific information about:
So, how long does data migration take? It can take anywhere from a few minutes to several days or weeks depending on how well-prepared the organization is for the migration and what’s being moved.
What are some data migration problems and challenges that an organization might face? A short list of some potential data migration challenges includes:
One of the first stumbling blocks that many data migration processes can run afoul of (especially when dealing with migrations from legacy systems or to entirely new architectures) is ensuring that the data is compatible with the destination systems and applications.
Different servers or software may use different operating systems or file management systems. This can be a problem because it can render data unusable on the target system if left as-is. To fix this, data sets may need to be converted to compatible formats (and then integrity-checked to verify that no errors were introduced during the conversion).
If the pre-migration assessment misses important data or applications that need to be moved, that can be a big problem for the organization. Unplanned-for data sets can alter the scope of a data migration project—creating delays and cost overruns.
This is why it’s important to ensure that there’s a complete map of all the data that needs to be migrated before starting on the data migration itself.
Can data be lost during data migration? Unfortunately, yes. There is always a risk of some data being lost during the migration process. However, this risk is usually minimal. In many cases, the lost data may not be mission-critical or it could be restored from a backup.
Data loss on a larger scale, or when data is lost without anyone noticing, can be a major problem. Following any data migration, it’s important to check the integrity of the data and see if anything has gone missing immediately after the migration.
Say there’s a report in data set A that pulls in a graphic from database B using a relative URL link to the folder in that database. However, data set A lives on database A, not database B. So, when that data set gets migrated to a new server, the link the report uses breaks, and the graphic doesn’t display correctly anymore. This would be an example of a cross-object dependency.
While a single file not showing a single image might not be catastrophic, imagine this happening to a mission-critical enterprise app. Odds are, it would bring one or more important business operations to a screeching halt—impacting performance, user experience, and productivity for the organization.
Finding, recruiting, and retaining skilled IT experts for functions like data migration can be prohibitively expensive. Many businesses lack the internal resources needed to build out a full-scale IT team to manage their IT infrastructure. Those that do have permanent IT staff may end up pressing IT personnel who have little to no experience specific to data migration into a migration management role.
Finding a qualified partner to help solve data migration problems and proactively work to smooth out the process can be invaluable for any business planning a major migration.
Whether the business is looking for a data migration partner or planning to handle the migration internally, there are a few key questions that need answers first:
RELATED: Is it Time to Get Rid of Your Legacy Systems?
Wondering how to do data migrations? Here are a few important steps to consider for any major data migration:
How much can your organization afford to spend on the migration process? This will often dictate the data migration tools and resources you use—as bigger budgets allow for more lavish solutions.
When preparing to move large data sets, it’s important to have help from an experienced migration partner. People who have a few migrations under their belt are more likely to be able to identify potential issues and help your business create an accurate estimate of what its migration strategy needs—smoothing out the process as a whole and potentially avoiding extra costs from data migration problems.
Establish which data sets to move and which ones can be left alone. Not everything always needs to be copied over.
Consider the compatibility of the data and apps being relocated with the new environment. Will the data need to be converted to work in the new application or server?
Which apps and data are people actually using in their day-to-day? If automated use metrics aren’t available, then polling end users and collecting their feedback can be valuable for prioritizing which apps and data to migrate. It can also reveal existing problems that may need correction after the migration.
Identify the key stakeholders in the organization, brief them on the data migration, and assign key roles and responsibilities as needed to fill out the migration team.
Is the logic of the migration sound? Testing the migration strategy with a mirror (i.e. copy) of the target production environment can help identify potential issues so they can be fixed before the actual migration happens.
Launch the migration strategy created previously. Once completed, validate the results to verify that all important data has been moved.
If decommissioning the older server or app, it should be shut down and disposed of.
Data migration testing is one of the most important aspects of any migration. What is data migration testing? It’s the process by which organizations test their migration strategy in a safe environment where failure won’t negatively impact the primary production environment.
Without migration testing, serious problems with the data storage environment, migration process, and migration tools may go undetected before it’s too late. So, setting up a copy of the target migration environment on a remote server and running a test is important!
By running a live test of the migration on a test server, businesses can easily find and fix data migration problems that might have been disastrous otherwise.
Need help setting up (or executing) a data migration strategy? Reach out to Systems X today to get started!
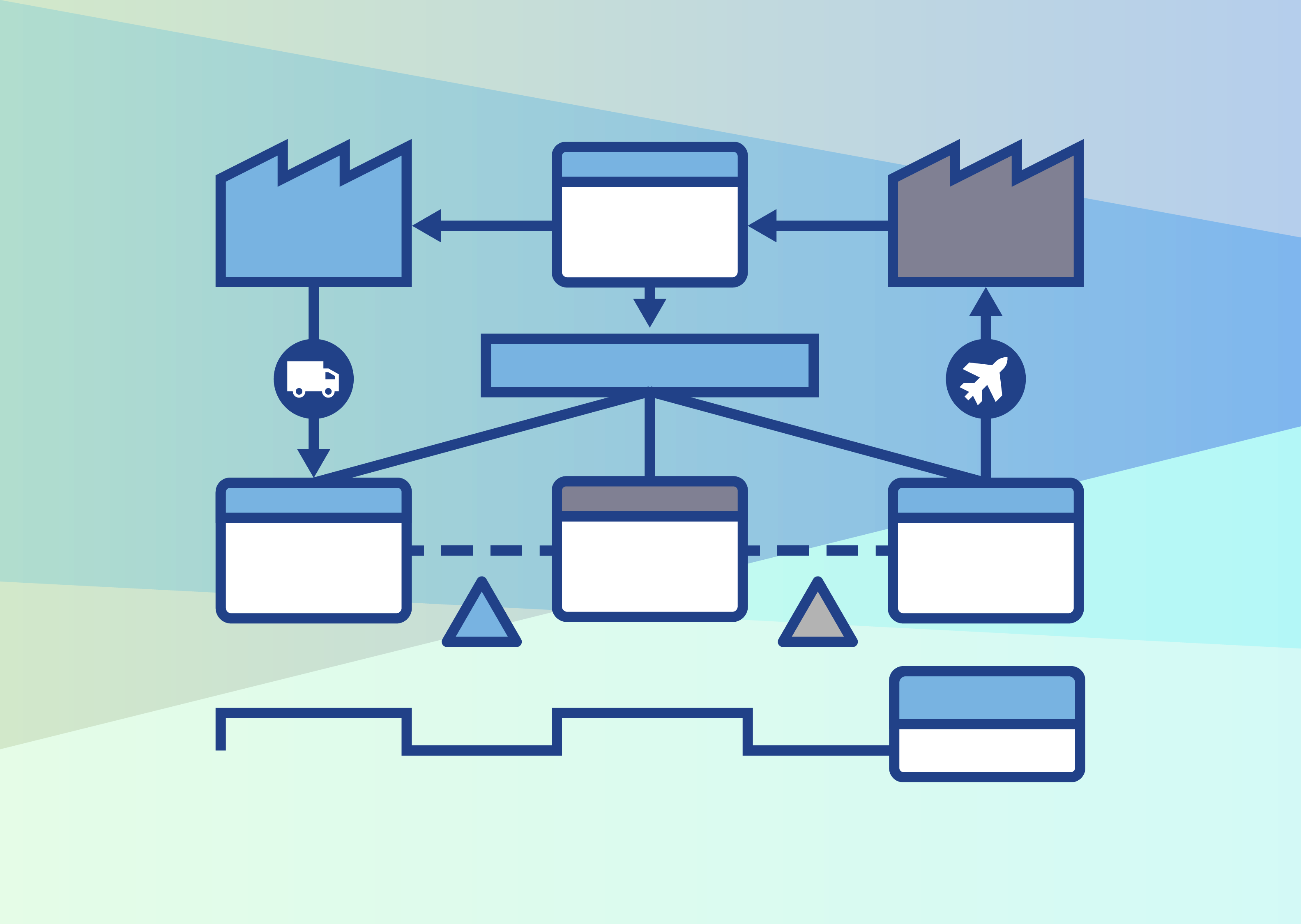
Organizations must optimize processes and improve operational efficiency for sustainable growth in today's competitive landscape. Value stream...

Enterprise Resource Planning systems, more commonly known as ERP systems, have become indispensableto users worldwide in the past decade.It’s a...

Exploring its Key Modules for Business Success with Support from Systems X Optimizing the supply chain is an undeniable priority in the...